About Acute Flaccid Myelitis
Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM) is a rare condition that occurs when a virus that is not polio but similar to polio (researchers think one such virus may be enterovirus D68, i.e. a cold or respiratory virus or the virus that causes hand, foot, and mouth disease) attacks the spinal cord. This often results in flaccid paralysis, weakness, neuropathy, fatigue, bowel/bladder problems, and more. AFM can affect multiple parts of the spinal cord, meaning it affects different parts of the body as well, depending on the person. But it most often results in quadriplegia or the paralysis of one limb. AFM is not as rare as it seems to be, but full recovery is rare. Contrary to media reports, washing your hands will not prevent you from getting AFM; it could prevent you from getting sick, but that is not guaranteed. If you get a cold, that does not mean you will get AFM, however.
Every two years in the fall, AFM is prominent in the news because there appear to be "spikes" of the disorder. This pattern is almost identical to the pattern Polio took on years ago. This pattern is due to the fact that illnesses go around at that time of year.
Acute Flaccid Myelitis became prominent in the news in 2014 when a number of children came down with a cold and then became paralyzed. As a result of this, there is a misconception that AFM first occurred in 2014, but this is misleading. AFM did not begin in 2014, as there are many known cases from before then, including Sarah Todd in 2010. Acute Flaccid Myelitis is a subset of Transverse Myelitis (TM), and there are a number of other related disorders, including Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO), and Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM). There is currently no known cure for any of these disorders.
Sarah Todd has Acute Flaccid Myelitis, and she wrote 5k, Ballet, and a Spinal Cord Injury, Determination, and Up and Down to raise awareness about this rare condition and share her story.
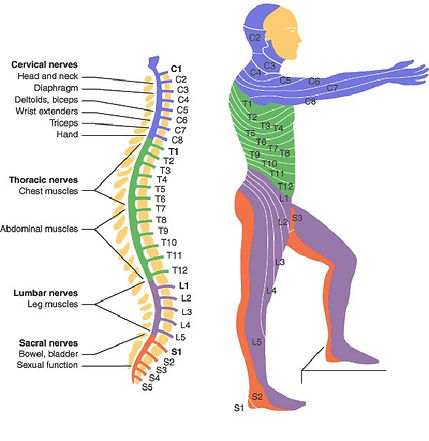
This picture shows the areas of the body that would most likely be affected if different sections of the spinal cord were damaged.
Anything below the section of the spinal cord that is damaged may also be affected, depending on if the injury is complete or incomplete.
Sarah Todd was affected from C2-T1.